Why did the Central Bank increase interest rates?
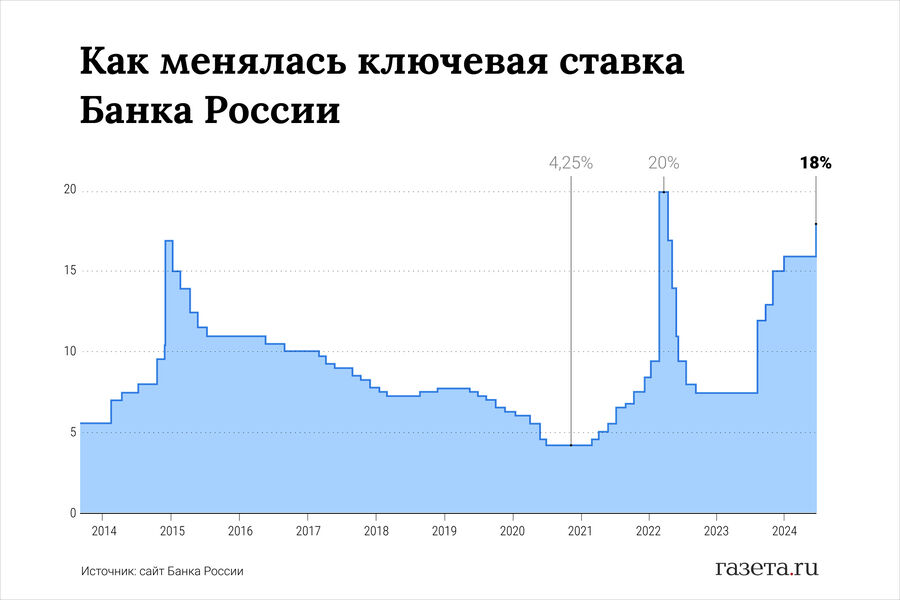
The Central Bank explained that the decision to raise interest rates was due to the acceleration of inflation in Russia. According to the regulator, the rate of price increase exceeded the April forecast and reached: 8.6% It is based on annual results for April-June 2024. Annual inflation in the January-March period was 5.8%.
“Growth in domestic demand continues to significantly outpace the ability to expand the supply of goods and services. Monetary policy needs to be tightened further for inflation to start falling again, and monetary conditions need to be significantly tighter than previously assumed for inflation to return to target,” the regulator said in a press release.
The Central Bank of Russia raised its inflation forecast for 2024 to 6.5-7.0%. Considering the current monetary policy, the Central Bank estimates that annual inflation will fall to 4.0-4.5 percent in 2025 and will be close to 4 percent in the future.
The regulator signaled to the financial market that the interest rate could be increased further at the next meetings. The central bank also raised its average key interest rate forecast for this year. 16.9-17.4% Between 15-16%.
Sovcombank chief analyst Mikhail Vasiliev believes that the Central Bank of Russia will again raise the key interest rate by 200 basis points at the next meetings (the reference meeting on September 13 or October 25), taking into account the Central Bank’s inflation forecasts and the average key interest rate will be raised by 20 basis points to 20%.
Alina Dzhus/socialbites.ca
What will happen to deposits?
Anna Volkova, director of retail business development at Sinara Bank, suggested in an interview with socialbites.ca that the Central Bank’s decision will help maintain the popularity of deposit and savings accounts, and will also provide additional money flows from Russians to banks.
“During periods when interest rates are high, people do not want to risk their savings, closely monitor deposit interest dynamics and try to choose the most profitable product. The flow of funds from traditional foreign exchange deposits in dollars and euros to deposits in yuan will continue.”
BitRiver financial analyst Vladislav Antonov told socialbites.ca that deposit rates began to rise a few weeks ago, and some Russian banks already give 19 percent and 20 percent on ruble deposits, subject to certain conditions. no more 1.5 million rubles. He does not expect Russians to try to deposit money in banks en masse after the interest rate hike.
“Among Russians, no panic is expected; in the last few months, increasing deposit interest rates have become commonplace. In any case, those who want to open a deposit will now carry money with them at a more favorable interest rate. It is worth remembering that not all Russians have free money to open a bank deposit,” the analyst admitted.
He stated that deposit interest rates will not decrease in the next three months and that the main trend is towards a reasonable increase.
Inflation is currently near its peak of 9.3% and will fall in the coming months to 7% by the end of this year and 4% by the end of 2025. So deposits are now really profitable. In the base case, we believe that the key rate of 18% will be the peak in this cycle, so you can open long-term deposits,” Vasiliev advised.
Candidate of Economic Sciences, teacher of Synergy Business School Daniil Petukhov allowed to increase the interest rates on deposits by another 1.5-2 points. That is, up to a maximum of 22% per annum.
What about the loans?
According to Petukhov, some banks’ consumer loan rates are already close to each other 40% annual and average market mortgage rate 29.5%. The expert expects loan interest rates to increase by 1.5-2 percentage points. After the Central Bank’s decision.
“Consumer loan interest rates have entered the barrier zone. For most Russians, the overpayment for such a product is so noticeable that they will not be able to take advantage of such offers as actively as before. There is a certain demand group here, but the lion’s share of the consumer loan market is “frozen”. When the Central Bank makes a rate cut, loan interest rates will start to fall, and then there will be a noticeable delay. These are market-specific things,” BitRiver analyst Antonov said.
Experts predict that the Russian credit market will cool down in light of the Central Bank’s decision.
“The general cooling is primarily due to the decline in the mortgage market after the cancellation of preferential programs from July 1. The consumer credit sector is still growing (although its pace has slowed down), the consumption boom has not disappeared – nominal wages are growing,” noted Anna Volkova, Sinara Bank’s retail business development director.
He predicts that demand for consumer loans will slow by the end of 2024, but there will be no sharp decline.
“We do not expect a decrease in interest rates in the coming quarters. We believe that the opportunity to reduce interest rates will open only in mid-2025, when inflation will steadily slow down towards the 4% target. Borrowers should be prepared for the fact that money in the economy will remain expensive for a long time and will probably become even more expensive,” Vasiliev concluded.
What will happen to the ruble?
Speaking to socialbites.ca, independent financial consultant Yulia Kuzmina said that the Central Bank’s decision will lead to a strengthening of the ruble in the short term and a fall in exchange rates. According to the consultant’s forecasts, the dollar could fall to 84 rubles or remain at 85 rubles, while the euro could weaken. 91-92 ruble and yuan – up to 10.5-11 According to Vasiliev, the ruble exchange rate will remain stable in the third and fourth quarters: the average yuan exchange rate will remain stable 12.2 ruble, dollar – 89 ruble, euro – 97 ruble
Kuzmina announced that on July 26 the dollar was worth 85 rubles, the euro was worth 93 rubles, and the yuan was worth 11 rubles.
“When interest rates are raised, the economy slows down, people and businesses take out fewer loans, buy fewer goods and services, because loans become more expensive, and when saving money on deposits, price growth also slows down. This strengthens the ruble exchange rate and weakens currencies,” Kuzmina said.
Ilya Fedorov, chief economist at BCS World of Investments, noted that the decision’s impact on the ruble was limited, as the exchange rate is now determined by the size of the current surplus as a result of falling imports.
“The population does not have a serious demand for foreign currency. In June, the public’s foreign exchange purchases fell by more than half. This also includes high interest rates on deposits,” the economist concluded.
What are you thinking?
Source: Gazeta
Ben Stock is a business analyst and writer for “Social Bites”. He offers insightful articles on the latest business news and developments, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of the business world.

