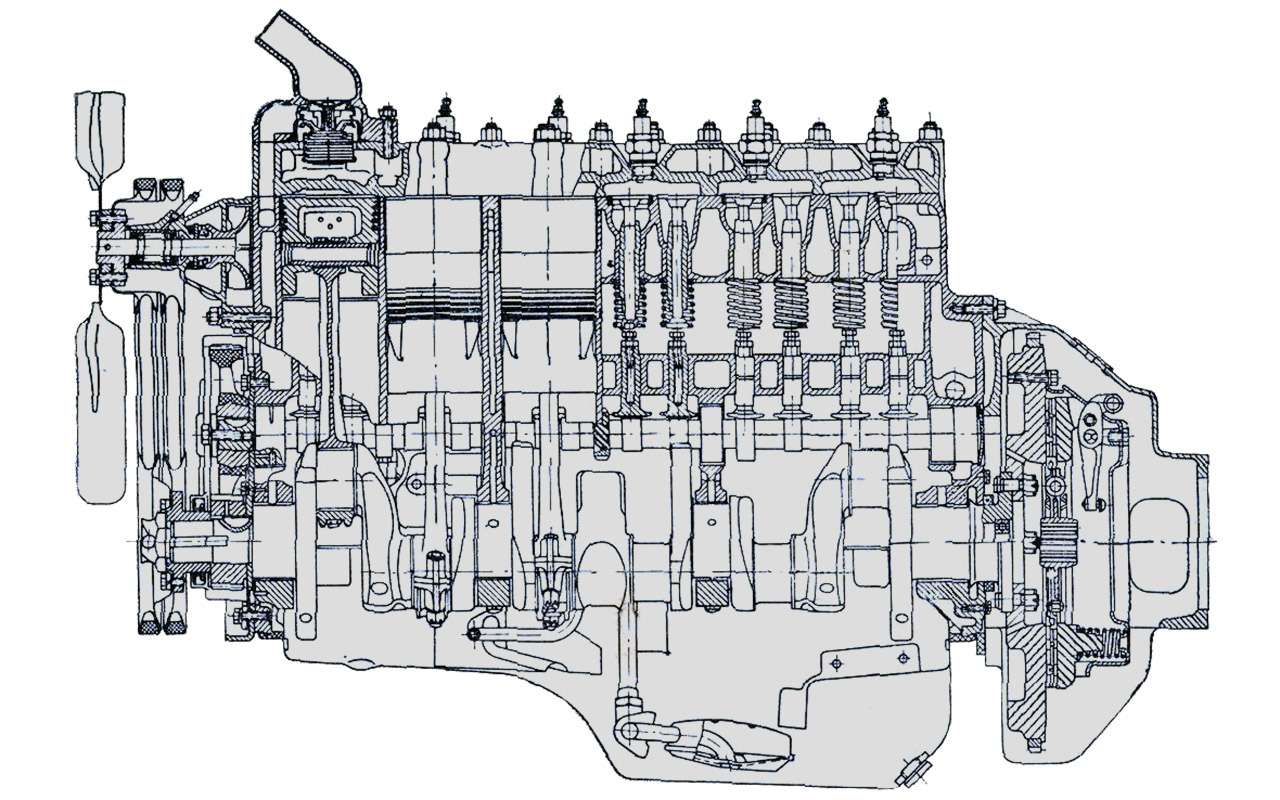
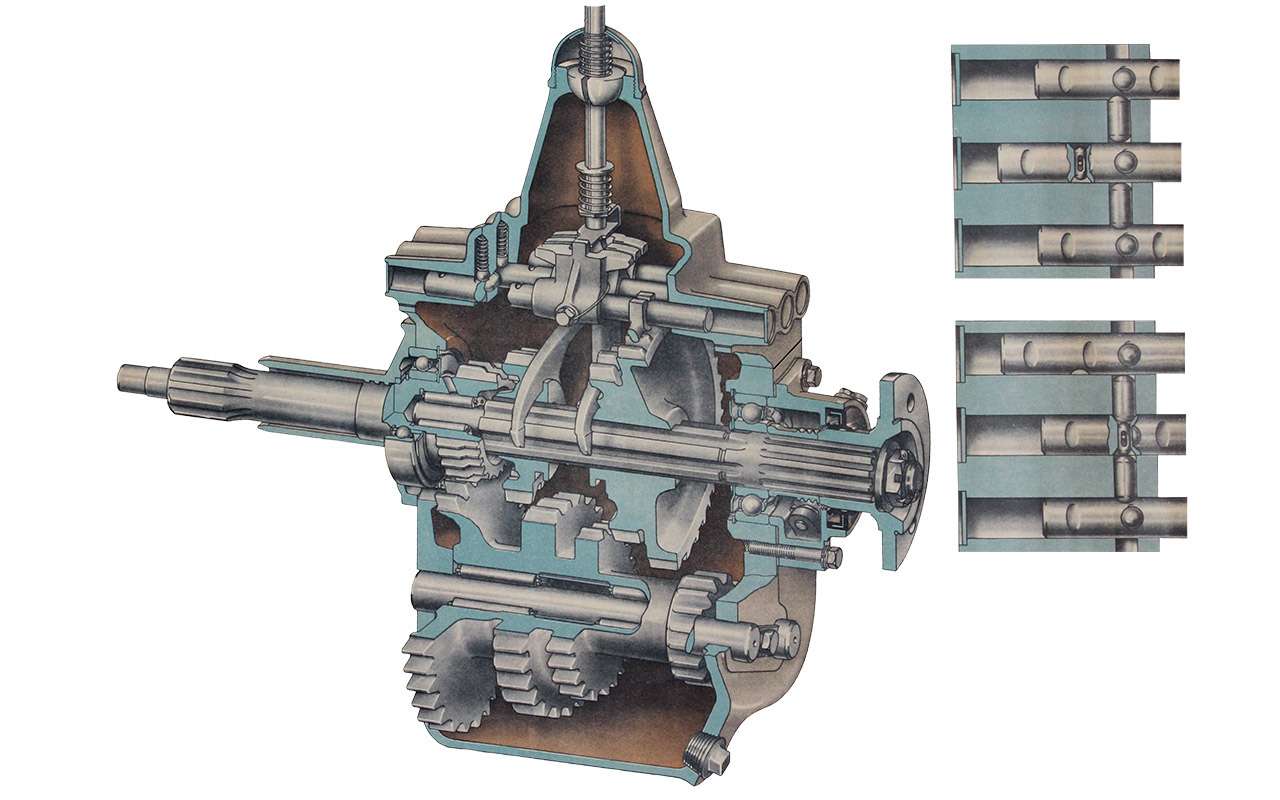
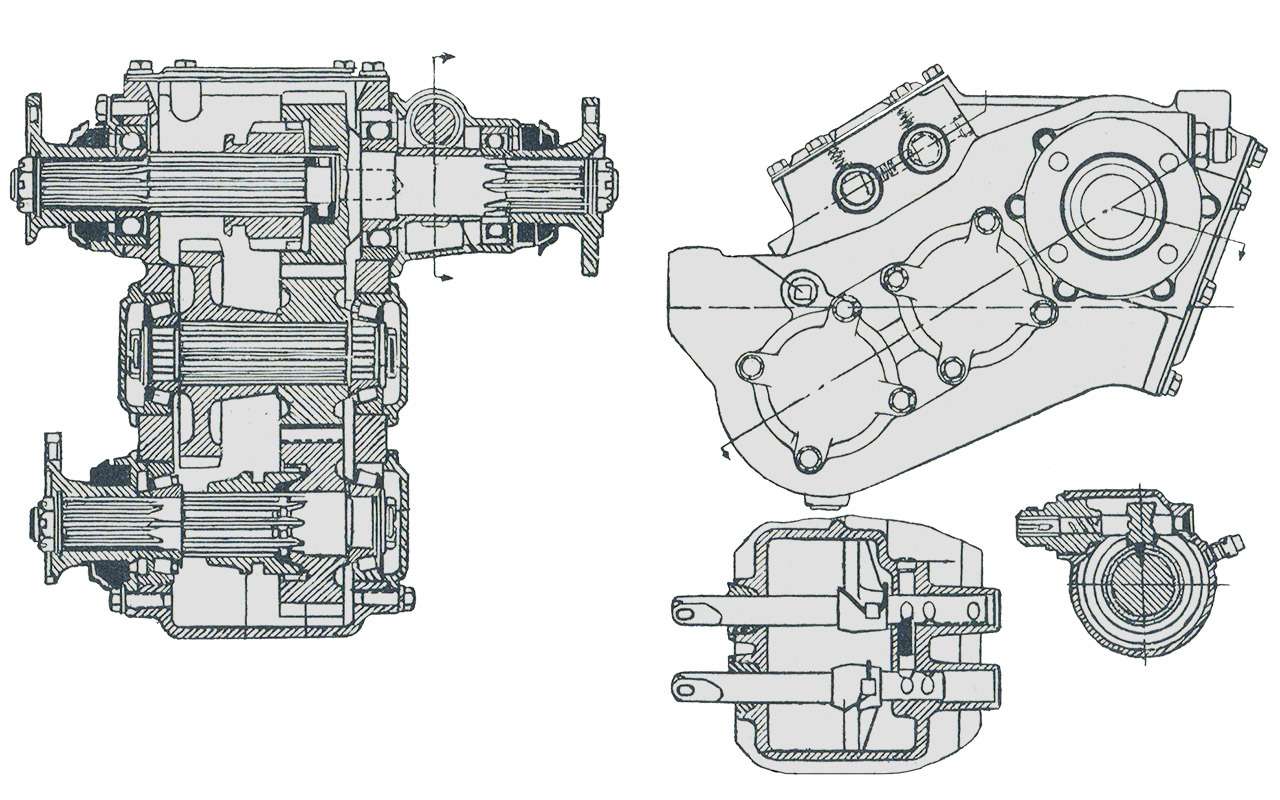
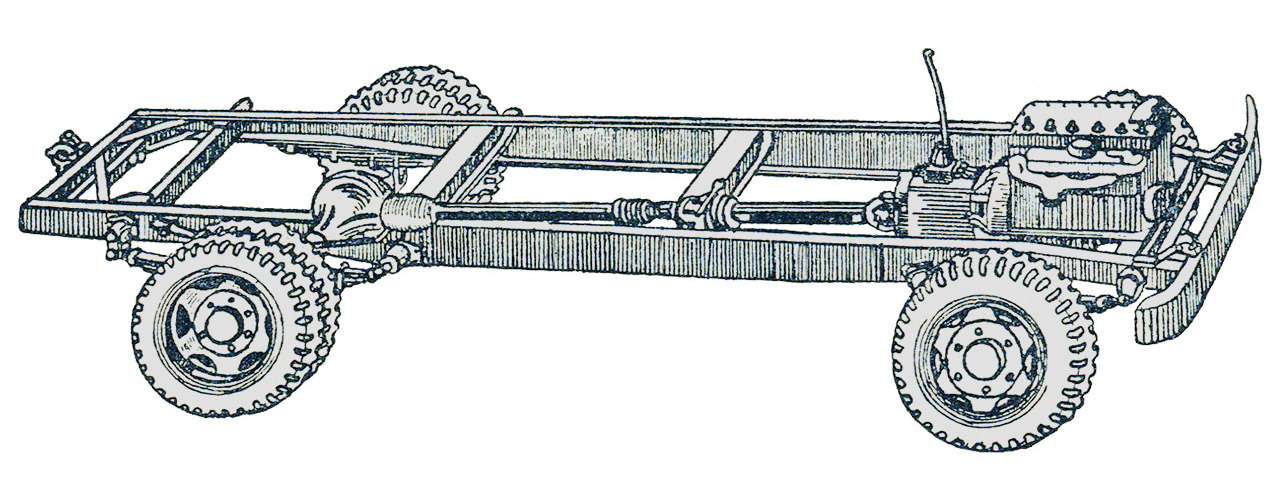
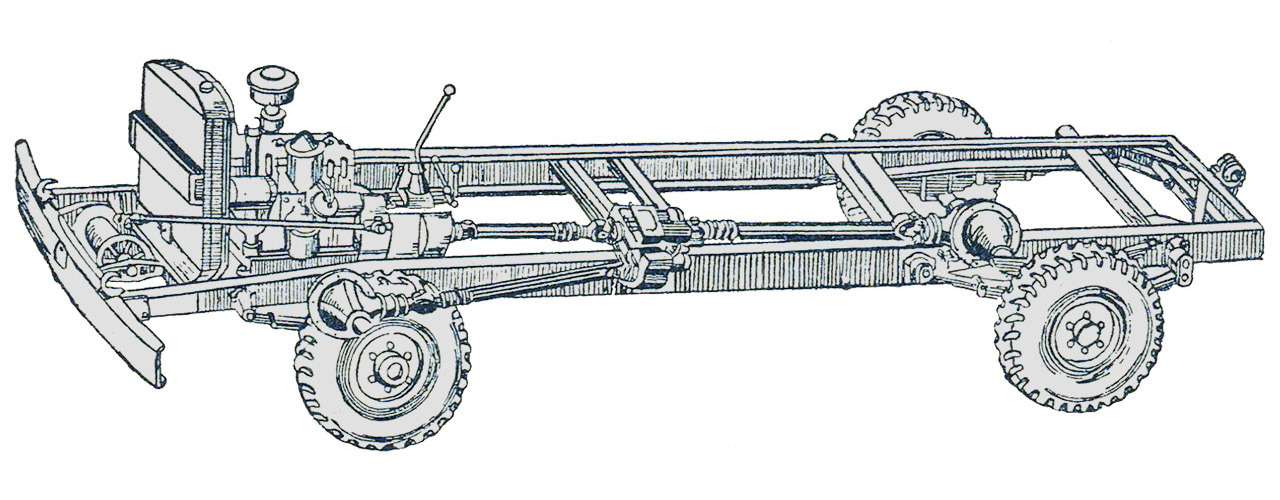
The development of four-wheel drive GAZ trucks began in the late 1930s. But the car went into production only in 1948. And this car was very different from the pre-war one. The design was based on the serial base GAZ-51.
Direct analogues of the 63rd were foreign trucks, already known in the USSR – they came during the Lend-Lease War.
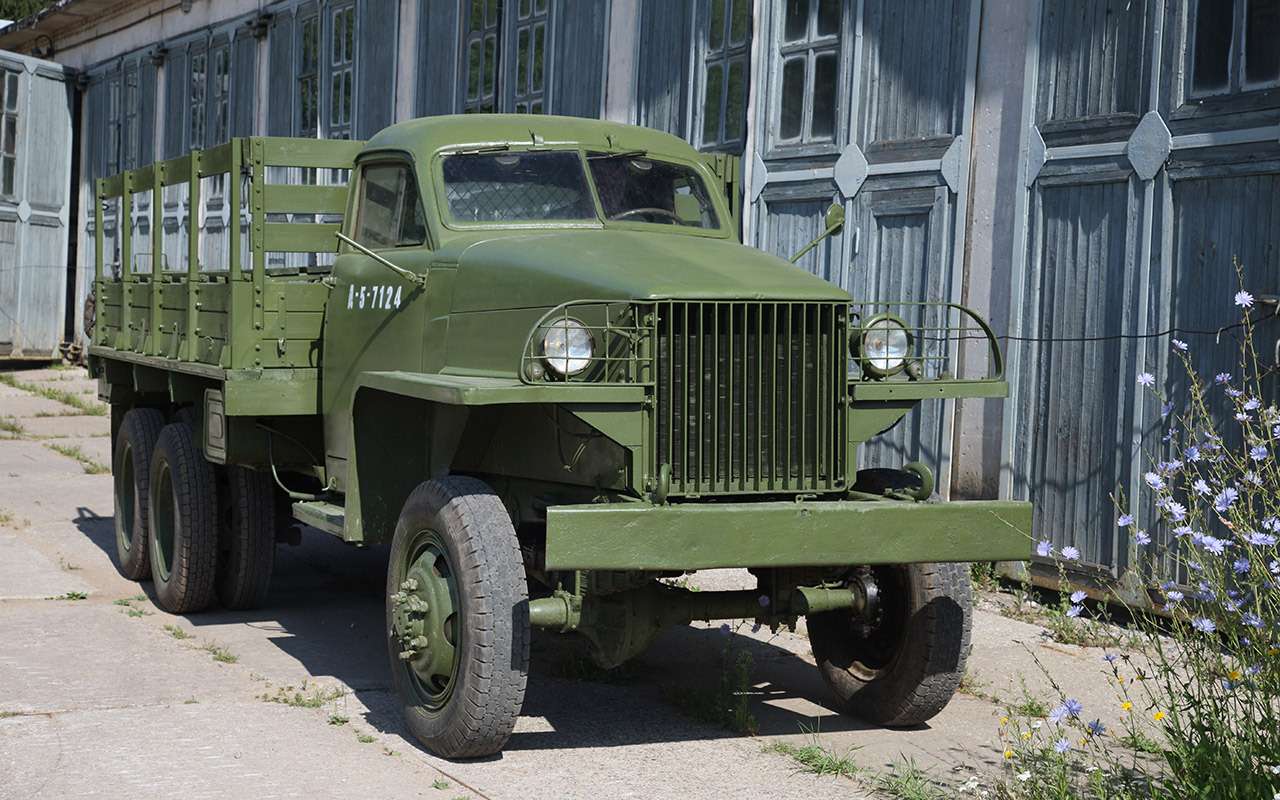
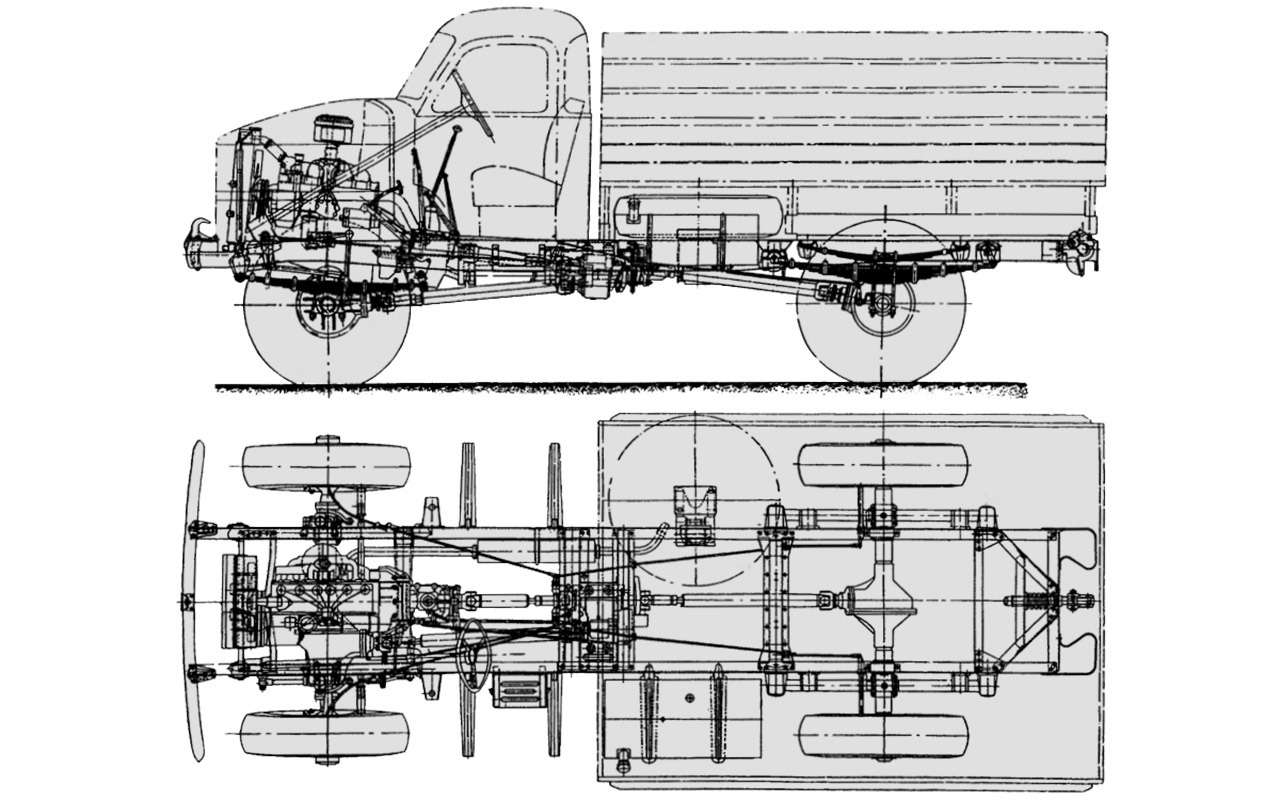
The 1500-2000 kg payload GAZ‑63 is a four-wheel drive version of the GAZ‑51. The base of the GAZ‑63 is the same as that of the GAZ‑51 — 3300mm, the track is in fact also 1588/1600mm (for the GAZ‑51 the rear is 1650mm). The ground clearance of the GAZ‑63 is 273 mm, more than that of the American counterparts known in the USSR, the Studebaker US6 and Chevrolet G7170 (they have 250 mm each).








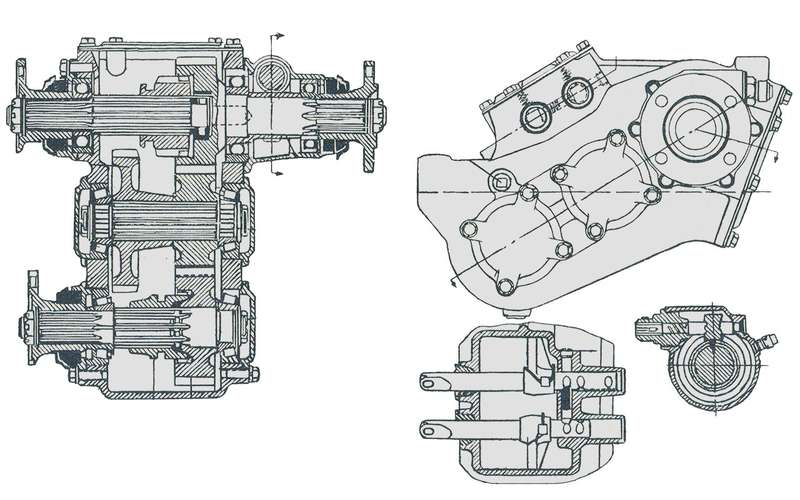


BRAT‑63
Maximum unification with the basic GAZ‑51 made it possible to create a post-war all-wheel drive version very quickly and inexpensively. Just after the war, such a car was needed, the army and the national economy.
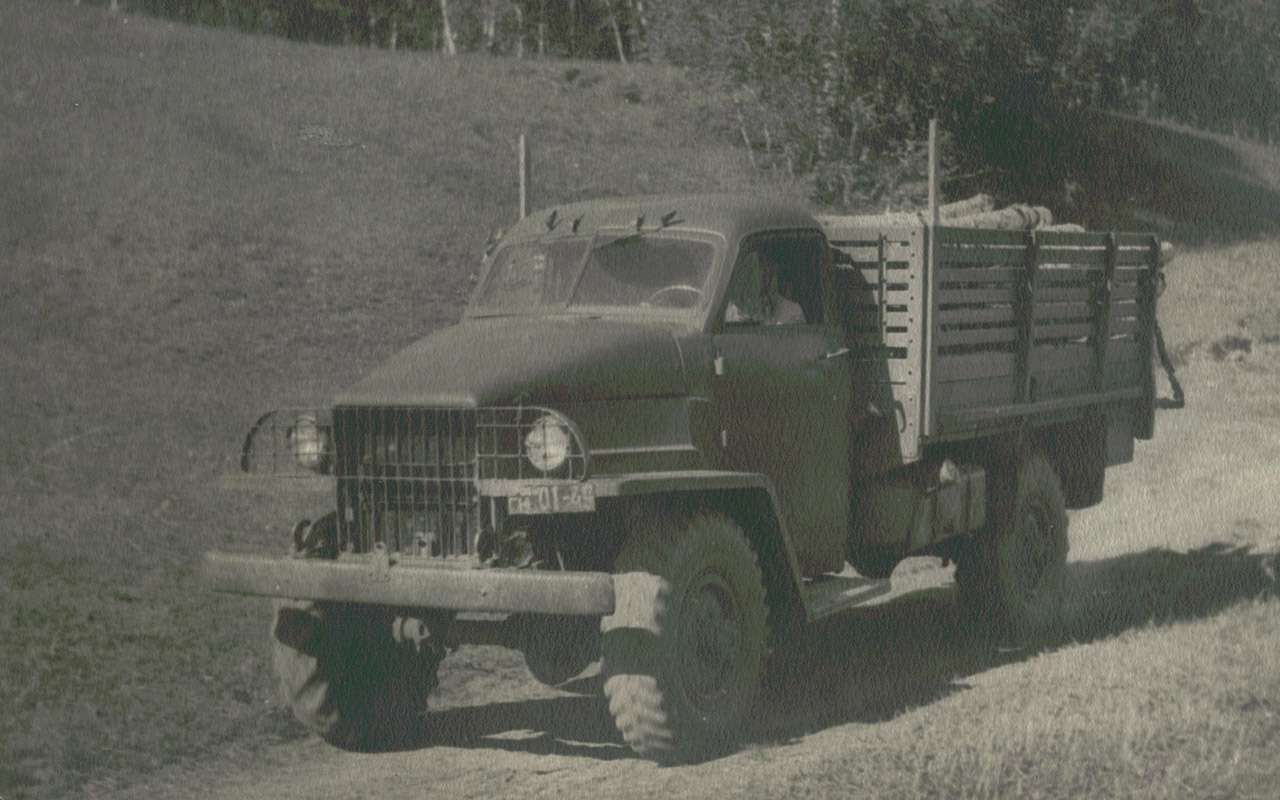
The car turned out to be quite successful, with excellent cross-country capabilities. True, because of the narrow gauge and high ground clearance on rough terrain, the GAZ‑63 had a tendency to roll over. But they accepted this in the name of unification with the base machine.
On the basis of the GAZ-63, truck tractors were created, and several factories made four-wheel drive buses. A total of 474,464 cars and Model 63 chassis were produced until 1968. Many of them are still alive.
- All the details about the American relatives of the ZIL-130 are here.
- The range of consumables under the TM “Za Rulem” is constantly expanding – you will also appreciate the quality of our products.
- “Behind the wheel” can also be read in Telegram.
We disassemble Gorky’s first mass-produced four-wheel drive truck for parts and details.